Key Points
- Understanding lateral epicondylalgia: Commonly known as tennis elbow, it is a chronic pain condition affecting the outer part of the elbow.
- Affected population: Tennis elbow commonly affects people aged 35-54, especially those in manual occupations involving repetitive hand movements.
- Physiotherapy benefits: Effective physiotherapy treatments include exercise, manual therapy, and a multimodal approach.
- Traditional and new management insights: Traditional management includes rest and corticosteroids, but new evidence supports exercise and manual therapy as more effective.
- Clinical implications: Physiotherapists should consider a patient’s prognosis and tailor treatments to improve outcomes, integrating new research findings.
What is lateral epicondylalgia? Commonly, what is it known as?
Lateral epicondylalgia (LE), more commonly known as tennis elbow, is a chronic musculoskeletal condition that causes pain and disability in the outer part of the elbow. This pain is typically associated with overuse of the forearm muscles and tendons, leading to inflammation and microtears at the lateral epicondyle, the bony prominence on the outer elbow.
Who suffers from tennis elbow?
Tennis elbow affects both men and women, most commonly between the ages of 35 and 54. While it is often associated with tennis players due to the repetitive wrist and arm motions in the sport, it also frequently affects people engaged in manual work involving repetitive arm and wrist movements. This includes occupations such as construction, painting, and factory work. Up to 50% of tennis players experience some form of elbow pain, with 75-80% of these cases being attributed to LE.
How is tennis elbow traditionally managed?
Traditional management of tennis elbow typically includes:
- Rest and activity modification: Reducing activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroid injections to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical modalities: Use of orthoses (braces) to support the elbow during activities.
- Surgery: Considered a last resort when conservative treatments fail, involving procedures to remove damaged tissue or repair tendons.
What does not work in the management of tennis elbow?
Certain treatments have been found to be less effective or ineffective in managing tennis elbow:
- Shock Wave Therapy (SWT): Studies show little or no benefit in reducing pain or improving function compared to placebo.
- Ultrasound therapy: Evidence indicates it is no more effective than placebo for pain relief.
- Friction massage: Often used in combination with other treatments, but alone it does not provide significant benefits.
What is the recommended management of tennis elbow?
Recent research highlights the effectiveness of exercise and manual therapy over traditional treatments. Key findings include:
- Exercise therapy: Eccentric exercises combined with other forms of physical activity have shown superior pain relief and functional improvement compared to passive treatments like ultrasound.
- Manual therapy: Mobilization-with-movement techniques provide immediate and sustained relief.
- Multimodal approaches: Combining exercise with manual therapy and other physical modalities can enhance outcomes and reduce the need for more invasive treatments.
How does Physiotherapy help with tennis elbow?
Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the management of tennis elbow by focusing on reducing pain, improving function, and preventing recurrence. Key physiotherapy interventions include:
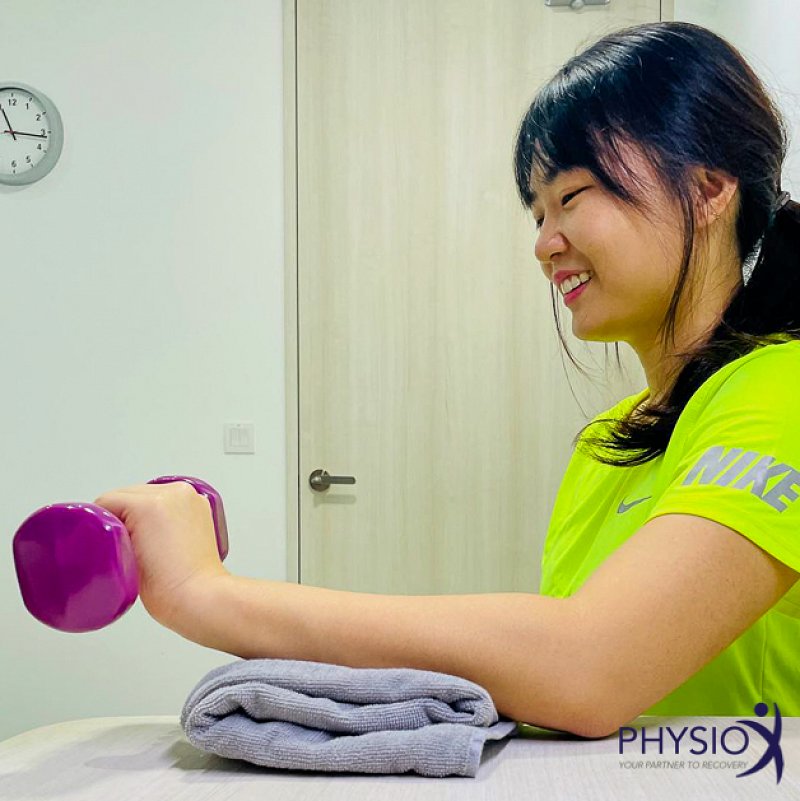
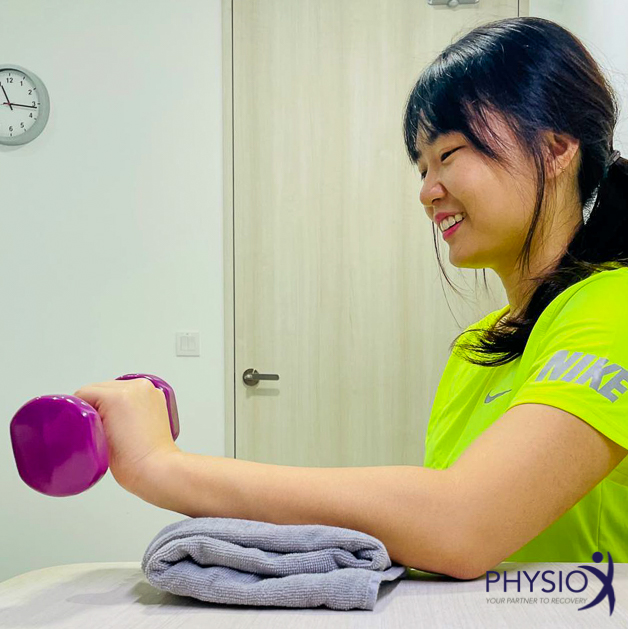
- Exercise therapy: Exercises, particularly those involving eccentric loading of the forearm muscles, are effective in alleviating pain and enhancing grip strength.
- Manual therapy: Techniques such as mobilization-with-movement can provide immediate pain relief and improve function.
- Education and advice: Educating patients about their condition and advising on activity modification and ergonomic adjustments can prevent further injury.
- Adjunctive therapies: Physiotherapy may also include ultrasound, laser therapy, and acupuncture as adjuncts to exercise and manual therapy.
If you are experiencing tennis elbow, consider the following management steps:
- Seek early Physiotherapy: Engage in a structured exercise program tailored by a physiotherapist to improve strength and flexibility.
- Modify activities: Reduce or adjust activities that exacerbate your symptoms.
- Use orthoses if recommended: Braces or straps can help reduce strain on the elbow during activities.
- Stay informed: Understand your condition and the importance of adhering to your treatment plan.
- Avoid over-reliance on medications: Use pain relief as needed but focus on long-term solutions like exercise and manual therapy.
As a Physiotherapist, apply these insights to improve patient outcomes:
- Implement evidence-based practices: Prioritize exercise and manual therapy as primary interventions.
- Educate patients: Inform patients about the nature of their condition and the benefits of physiotherapy.
- Tailor treatments: Customize treatment plans based on individual patient needs and prognostic factors.
- Monitor progress: Regularly assess pain and function to adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Stay updated: Keep abreast of the latest research to provide the best care possible.
Conclusion
Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylalgia, is a common condition affecting the elbow. While traditionally managed with rest, medication, and physical modalities, recent research emphasizes the effectiveness of exercise and manual therapy. As a patient, understanding your condition and following a structured physiotherapy program can lead to better outcomes. Physiotherapists should incorporate these findings into their practice to enhance patient care.
Ref:
Bisset, L. M., & Vicenzino, B. (2015). Physiotherapy management of lateral epicondylalgia. Journal of Physiotherapy, 61(4), 174-181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphys.2015.07.015
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best treatment for tennis elbow?
The best treatment involves a combination of exercise therapy, manual therapy, and patient education. These approaches have been shown to provide effective pain relief and functional improvement.
How long does it take to recover from tennis elbow?
Recovery time can vary, but with a structured physiotherapy program, significant improvements can often be seen within 6-12 weeks. Consistent exercise and activity modification are crucial for long-term recovery.
Can tennis elbow heal on its own?
While some cases may improve with rest and activity modification, physiotherapy is often necessary to address underlying issues and prevent recurrence. Without treatment, symptoms can persist or recur.
Is surgery necessary for tennis elbow?
Surgery is rarely needed for tennis elbow and is typically considered only when conservative treatments fail. Most patients benefit from physiotherapy and other non-invasive treatments.
What exercises are recommended for tennis elbow?
Eccentric exercises for the forearm muscles are highly recommended. These exercises should be performed under the guidance of a physiotherapist to ensure proper technique and effectiveness.